Summer Container Gardening Ideas: Potted Plants For Small Spaces
Container gardening allows you to grow plants in pots, planters, and other vessels rather than directly in the ground. It is a great solution for those with limited yard space. Container gardening offers numerous benefits like portability, control over soil conditions, reduced weeds and pests, and the ability to create miniature gardens. However, it also poses some challenges like frequent watering and fertilizing, potential root overcrowding, and overwintering logistics. This article will provide tips and ideas for successfully growing a container garden this summer, including choosing containers and soil, selecting plants suited for pots, maintaining optimal conditions, and troubleshooting problems. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge to create beautiful and productive container gardens even in the smallest outdoor spaces.
Source: https://homesteading.com/container-gardening-pros-cons/
Choosing the Right Container
When selecting a container for your summer container garden, you’ll need to consider factors like material, drainage, and size. Popular materials for pots and planters include plastic, ceramic, and wood.
Plastic planters like resin pots are lightweight, inexpensive, and come in many shapes and sizes. Look for thicker plastic that won’t become brittle and crack over time. Ceramic and terra cotta pots are attractive but heavier and more prone to cracking if exposed to freezing temperatures. Wood planters like wooden planters add a natural touch but will deteriorate over time.
Be sure any container has drainage holes in the bottom to prevent soggy soil and flooded roots. Consider the size of your chosen plants – a very small plant in a huge pot with too much soil may struggle to thrive. For a mixed planter, choose a pot at least 10-12 inches wide and 10-12 inches deep. For a single large plant like a tomato, opt for at least a 5 gallon pot or wider than 12 inches.
Soil Mix
The soil mix is one of the most important factors for successful container gardening. Using the right soil provides nutrients for plants to thrive and proper drainage to prevent soggy roots. The ideal container soil is lightweight and fast-draining but also moisture-retentive.
A homemade mix of 1 part compost, 1 part potting soil, and 1 part perlite or vermiculite is recommended. The compost provides nutrients, the potting soil offers moisture retention, and the perlite/vermiculite improves drainage. You can also purchase premixed potting soils made for containers.
In addition to the soil base, containers require more frequent fertilization than in-ground gardens. Every 2-4 weeks during the growing season, use a water-soluble fertilizer made for containers by following the label instructions.
Taking the time to prepare quality soil will pay off with healthier plants and larger yields for your container garden.
Sun Exposure
Getting the right amount of sun is crucial for container plants to thrive. Most vegetables and flowering annuals need at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day. Leafy greens and herbs can get by with 3-4 hours of sun. For containers in shady spots that get less than 3 hours of sun, focus on shade-loving plants.
There are solutions for placing containers in shady areas. Move pots around to follow the sunlight throughout the day. Prune overhanging branches to open up the area to more sun. Use light-colored containers that reflect sunlight. Supplement with grow lights if needed. Choose shade-loving varieties like begonias, impatiens, and coleus that are adapted to lower light.
Pay attention to the sun requirements of each plant and group those with similar needs together. Monitor sunlight over the course of a day to ensure containers are getting adequate exposure based on the plants’ preferences.
Watering
Proper watering is crucial for container gardening. Since potting soil dries out faster than ground soil, containers usually need watering at least once a day during hot summer months. Pay attention to signs of under or overwatering.
Check the soil moisture daily by sticking your finger into the soil. Water when the top inch feels dry. Apply enough water so it drains from the bottom of the container. This ensures the entire root zone is hydrated. In warm weather, containers may need watering twice a day.
Underwatered plants will wilt or drop leaves. Leaves may turn brown at the edges or curl up. Overwatered plants will also wilt as roots suffocate. Yellowing leaves, fungi growth, and foul odors are other signs of overwatering. Allow the soil to partially dry between waterings.
Ideally, water early in the day so excess moisture can evaporate by nightfall. This helps prevent fungal diseases (source). Consider automatic drip irrigation for frequent watering while away (source).
Choosing Plants
When selecting plants for container gardening, especially in small spaces, it’s important to choose compact or dwarf varieties that will not outgrow the pot. Some great options include:[1][2]
- Tomatoes – Choose determinate, bush, or patio varieties like Better Boy Bush Hybrid or Patio Choice Yellow.
- Peppers – Opt for compact varieties like Sweet Banana or Red Cherry Sweet.
- Eggplant – Slim Jim and Little Fingers are small, skinny eggplant cultivars perfect for pots.
- Herbs – Many herbs like thyme, oregano, chives grow well in containers.
- Lettuce – Looseleaf and oakleaf lettuce varieties can thrive in pots.
- Flowers – Choose short, compact annuals like marigolds, petunias, or zinnias to add color.
You can mix flowers, herbs, and vegetables together in attractive combinations. Companion planting can also help maximize the yield in a small space. For example, pairing beans with carrots encourages growth for both plants. Other compatible companions are tomatoes with basil, onions with kale, and cabbage with petunias.[1]
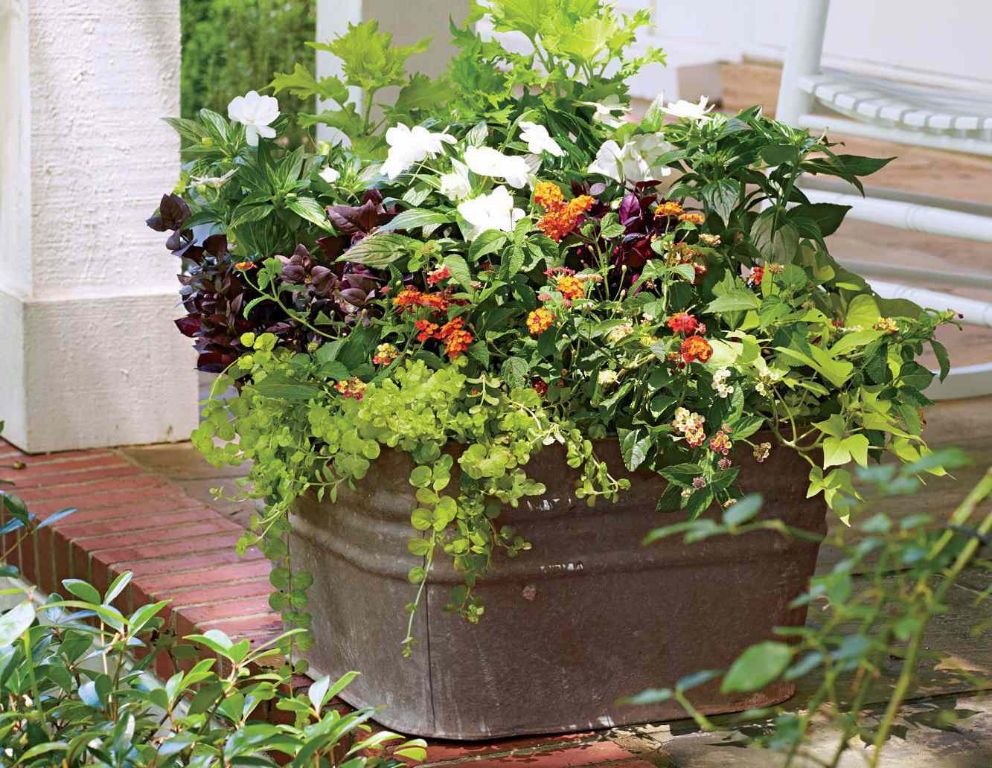

With some creativity and strategic plant choices, you can create a bountiful container garden almost anywhere.
[1] https://miraclegro.com/en-us/projects-planning/best-container-plant-combinations.html
[2] https://blog.jungseed.com/container-gardening-for-beginners/
Planting and Maintenance
When planting seeds or transplants in containers, make sure the container has drainage holes to prevent waterlogging. Fill the container with potting mix so it reaches about 1 inch below the rim, then sow seeds according to package directions or plant transplants at the same level they were growing in their starter pots (source). Water well after planting and check soil moisture regularly, watering when the top inch becomes dry.
Fertilize container plants every 2-4 weeks during the growing season using a water-soluble fertilizer mixed at half-strength. Prune back any leggy or dead growth regularly to keep plants compact and encourage new growth (source). Troubleshoot any issues like wilting or pests right away. Make sure containers have adequate drainage and don’t allow plants to become pot-bound. Address any disease or pests following organic recommendations.
Small Space Solutions
Container gardening is a great option for those with limited outdoor space. Vertical gardening and hanging baskets allow you to maximize every square inch. Here are some small space container gardening ideas:
Hanging Baskets
Hanging baskets are a beautiful way to add instant color and greenery to small patios, balconies, and porches. Choose lightweight potting soil and trailing plants like ivy geraniums, petunias, lobelia, and flowering vines. Be sure to hang baskets where you can easily access them for watering and care. Just make sure to properly support any hanging baskets so the weight doesn’t compromise structures or brackets.
Vertical Gardening
Utilize walls, fences, railings and trellises to grow plants vertically. This expands your planting space and allows you to grow vining crops like beans, cucumbers, peas, and tomatoes on a strong trellis. You can also affix stacked pots or special vertical planters to maximize planting in tight spots.
For example, attach planter boxes or stacked pots to balcony and patio railings. Or mount wall-mounted planters to grow an assortment of herbs, greens, and strawberries (source).
Tiered Planters
Multi-level planters are an efficient way to grow lots of plants in a small footprint. Choose durable planters with built-in shelves to divide planting space. Position larger plants on bottom shelves and smaller pots on upper tiers. This creates a beautiful vertical display.
For balconies and patios, look for tiered planters that mount securely on railings. They take advantage of vertical real estate to maximize planting options (source).
Overwintering
When the weather turns cold, many container plants need to be brought indoors. According to PlantTalk Colorado, containerized plants are susceptible to extreme cold and frequent freeze-thaw cycles, so they should be moved to a protected area for the winter.
First, inspect plants carefully for pests before bringing them inside. Give them a good rinse to remove dust and debris. Prune back leggy growth and remove dead or damaged foliage and stems. This helps direct the plant’s energy into new spring growth.
Find the sunniest indoor spot possible. A south or west facing window is ideal. Supplement natural light with grow lights if needed. Reduce watering frequency since plants grow slower in winter. Allow the soil to partially dry out between waterings. Maintain humidity around 50-60% to prevent leaf scorch.
According to Patuxent Nursery, the keys to overwintering container plants successfully indoors are proper light, temperate conditions, humidity, and reduced watering.
Conclusion
Container gardening offers many benefits and can be a great way to grow plants even in a small outdoor space. The key tips covered in this article include choosing the right sized container with drainage holes, using a quality potting mix, ensuring adequate sun exposure, proper and consistent watering, selecting plants suited for containers, and providing ongoing maintenance like pruning and deadheading. Proper overwintering methods are also important for preserving containers and plants when bringing them indoors.
The advantages of growing plants in pots include being able to move them around to capture sunlight or create focal points in the garden. Container gardening also provides flexibility to grow a wide variety of plants that may not thrive directly in the ground. It is an accessible method even for beginners, with the ability to control soil quality, drainage, and other factors in a pot. For those with limited yard space, container gardening maximizes plant options and decor. With some planning and preparation, gardens can be enjoyed all season long through this versatile gardening method.