Sustainable Garden Design: Eco-Friendly Practices For Your Yard
Sustainable garden design incorporates environmentally friendly practices that benefit the health of the planet. The main goal is to create an outdoor space that works in harmony with nature rather than fighting against it (https://rotasversatil.com/sustainable-garden-design-a-blueprint-for-environmental-stewardship/). This involves making careful choices to conserve resources like water and energy, reduce waste, nurture the soil, and support biodiversity. Thoughtful planning and design can help your garden thrive with minimal intervention. Choosing native plants, implementing smart water systems, composting, and eliminating pesticides are some key sustainable strategies. By taking an eco-friendly approach, you can reduce your environmental impact and create a self-sufficient sanctuary right in your own backyard.
Benefits
Eco-friendly landscape design provides numerous benefits for homeowners and the environment. According to CalRecycle, sustainable landscapes help conserve water, improve soil health, reduce waste generation, and require less maintenance and labor.
Sustainable landscaping techniques can help protect the environment in several ways. Planting native species and using organic methods creates healthier soil and plant life while reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides that can contaminate waterways. Wise water usage through drip irrigation, rain barrels, and drought-tolerant plants also conserves precious water resources.
In addition to environmental benefits, sustainable landscapes can save homeowners money over time. Once established, these yards require less frequent mowing, pruning, and watering. Organic methods and native plants are also less costly than purchasing and maintaining thirsty grass lawns. Focusing on perennials versus annuals further reduces yearly plant purchases and labor.
Design Considerations
When designing a sustainable garden, careful consideration should be given to placement, layout, and plant selection (Sustainable Landscape Design Principles). Proper site analysis and planning from the start can help maximize sunlight, promote water conservation, and create an efficient garden ecosystem.
Garden placement is key. Locate vegetable gardens and sun-loving plants in areas that receive at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily. Shade-tolerant varieties can be positioned in partly shaded zones. Arrange plants with similar water and sunlight needs together for ease of care (Principles of a Sustainable Landscape Design).
An eco-friendly layout utilizes space efficiently. Group plants densely to help retain moisture in the soil. Use trellises, arbors, and vertical gardening techniques to maximize planting area. Incorporate organic and geometric shapes for visual interest. Pathways should facilitate accessibility and maintenance.
When selecting plants, choose non-invasive native species that are drought tolerant and pest resistant. Diversity above and below ground promotes a healthy ecosystem. Mix annuals and perennials, trees, shrubs, groundcovers, vines, and grasses. Underplantings like clover or creeping thyme help suppress weeds.
Soil Health
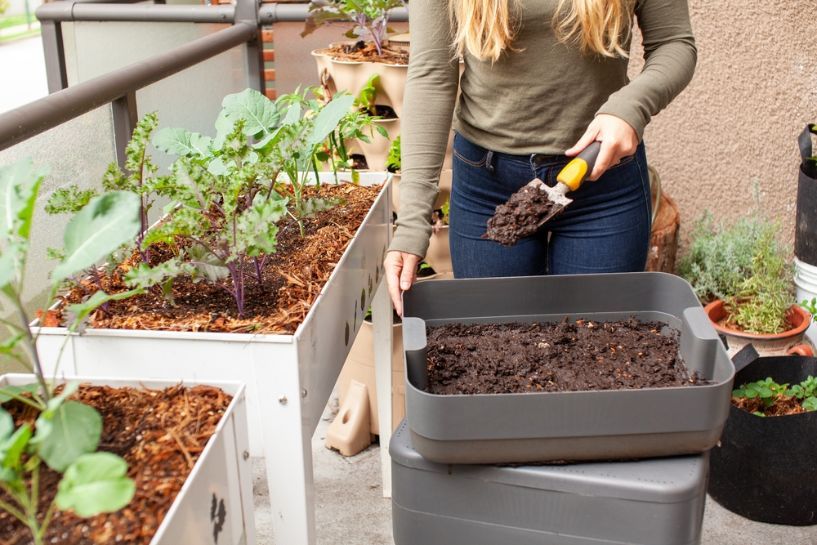

Healthy soil is the foundation of an eco-friendly garden. Focus on improving soil health through organic practices like composting, mulching, and cover cropping. Compost helps nourish plants by providing nutrients and encouraging microbial activity in the soil (https://rodaleinstitute.org/blog/10-ways-organic-improves-soil-health/). Mulch retains moisture, prevents weeds, and adds organic matter as it decomposes. Cover crops like clover or rye planted in the off-season help suppress weeds, prevent erosion, and replenish nitrogen when tilled into the soil (https://www.farmers.gov/conservation/soil-health). Focusing on improving the soil sets up your garden for success by creating the ideal environment for plants to thrive.
Water Conservation
Water is a precious resource, especially in arid climates. There are several ways to reduce water usage in your garden and landscape while still maintaining lush and vibrant plants.
Rainwater harvesting is an effective water conservation method. You can collect rainfall from rooftops and store it in rain barrels or cisterns to use for watering your garden later. Properly sized rainwater harvesting systems can provide most or all of the water your garden needs after initial establishment.1
Using efficient irrigation methods such as drip irrigation, microsprinklers, or soaker hoses rather than overhead watering saves significant water by minimizing evaporation, runoff, and overwatering. These methods deliver water directly to plant roots through slow, targeted dripping or spraying.2
Choosing native and drought-tolerant plants that are well-adapted to your climate is another easy way to save water. Once established, these plants require little to no irrigation beyond normal rainfall. Grouping plants with similar water needs together in hydrozones also optimizes water use efficiency.3
Organic Pest Management
Employing organic pest management techniques is key for an eco-friendly garden. There are several effective methods for controlling pests without using chemical pesticides.
Companion planting can help repel pests. For example, planting onions and carrots together will help deter carrot flies. Marigolds also repel certain pests like nematodes. Interspersing plants that attract beneficial insects like ladybugs can also control pests Organic Garden Pest Control – Roots and Refuge.
Using Bacillus thuringiensis (BT) is an organic alternative to chemical pesticides. BT is a naturally occurring bacterium that kills leaf-eating caterpillars when they ingest it, but is not harmful to people or beneficial insects. It can be purchased as a liquid concentrate and sprayed directly on plants when pests are first spotted.
Attracting beneficial insects like ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitoid wasps can be an effective part of an organic pest control strategy. Providing habitat like wildflowers and native plants will draw in these predators to naturally control pests.
Reduce Waste
A sustainable garden should aim to reduce waste as much as possible. Here are some tips for reducing waste:
Composting is one of the best ways to reduce waste in the garden. Food scraps, leaves, grass clippings and other organic materials can be composted rather than sent to the landfill. Compost enriches the soil, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers. According to the National Wildlife Federation, composting leaves and grass clippings alone can reduce waste by 20-30%.
Look for opportunities to repurpose materials rather than buying new. For example, toilet paper rolls, plastic bottles, and containers can be repurposed as seed starters or mini greenhouse domes. Egg cartons are great for starting seedlings. Get creative with what you might otherwise throw away.
Avoid chemical pesticides, fertilizers, and cleaners. These not only create waste from their packaging but can also pollute water and soil. Consider organic approaches to pest and weed control.
Energy Efficiency
There are several ways to design an energy efficient garden. Using solar-powered lighting and pumps can reduce reliance on the electrical grid. According to 5 Smart Tips For An Energy-Efficient Garden, solar lights and pumps that run on the sun’s energy are a smart choice.
It’s also recommended to use hand tools instead of gas-powered tools when possible. The website 5 Efficient Ways to Save Energy and Water in the Garden suggests avoiding gas-guzzling mowers and trimmers and using manual tools like push mowers and hand shears. This saves on fuel and reduces air and noise pollution.
In general, designing a garden focused on energy efficiency will reduce environmental impact and utility costs over time. Strategies like solar power, manual tools, and native plant choices create a sustainable landscape.
Native Plants
Native plants provide many benefits for sustainable gardens. According to the Audubon Society, native plants offer nectar for pollinators including hummingbirds, bees, butterflies, moths, and bats. They also provide shelter for mammals and birds (https://www.audubon.org/content/why-native-plants-matter).
The USDA notes that native plants help improve air quality because they do not require mowing or excessive maintenance. They also sequester carbon in the soil, helping to mitigate climate change (https://www.fs.usda.gov/wildflowers/Native_Plant_Materials/Native_Gardening/index.shtml).
Some great native plants for sustainable gardens include coneflowers, butterfly weed, cardinal flower, and buttonbush. It’s important to choose native species that are adapted to your specific region and climate. The California Native Plant Society recommends selecting plants that are endemic to your area, as they will be best suited to local conditions and support native wildlife (https://www.cnps.org/gardening/why-natives/benefits-of-california-native-plants).
Conclusion
Sustainable gardening practices take into account the health of the environment, reducing waste, conserving water and other resources. The aim is to create productive gardens that balance nature’s needs with your own. By implementing strategies like water conservation, reducing pesticide and synthetic fertilizer use, composting, energy efficiency, planting native species, and protecting pollinators and other wildlife, you can create a vibrant habitat and productive garden. The future of gardening lies in finding new ways to provide bountiful harvests while nurturing the Earth and conserving our shared resources. With your help and creativity, we can cultivate both healthy soil and thriving communities, beautifying the planet for generations to come.
Call to action: Think small to make a big difference. Start with a few sustainable practices that fit your climate, landscape, skill level, and interest. As your experience grows, expand your sustainable gardening efforts for even more benefits.