Diy Urban Garden Design Ideas For Urbanites
Urban gardening has become increasingly popular in recent years, especially among city dwellers and urbanites. According to research, there has been a steady increase in gardening retail since 2018 with revenue growing from upwards of 4% to almost 9% in 2020. Consumers have become more interested in do-it-yourself urban gardening and growing their own food amid the pandemic (https://in-sight.symrise.com/article/trend-perspectives-why-urban-gardening-has-take-off-in-popularity). Urban gardens allow people to grow fresh produce and herbs even if they don’t have access to large plots of land. Gardening in an urban setting comes with unique challenges but can also provide many benefits. Urban gardens can help improve biodiversity, reduce a person’s carbon footprint by growing food locally, and provide relaxation or a creative outlet in a busy city environment.
Space Optimization
When it comes to urban gardening, utilizing vertical space and compact footprints is key for maximizing productivity in a small area. Vertical gardening takes advantage of walls, fences, railings, and other vertical structures to grow plants upward rather than outward. Simple solutions like wall-mounted planters and hanging gardens allow you to use vertical space above and around existing planting beds. For example, you can install shelves above your garden bed to double the planting space. Hanging planters also work well on railings, walls, patios, and even windows. Going vertical with vining plants like beans, cucumbers, and tomatoes can also optimize horizontal growing space. Using compact plant varieties, intercropping, and succession planting are other useful techniques for small space vegetable gardening. With some creativity, it’s possible to grow a thriving urban garden even in the smallest outdoor nook.
Soil Considerations
Soil quality is crucial for thriving plants, especially in urban gardens with space constraints. When gardening in containers or raised beds, you’ll want to use a high-quality potting mix rather than standard garden soil (1). Potting mixes are lightweight, fluffy blends designed to drain well and provide nutrients in a limited space. Look for mixes with a blend of peat moss or coconut coir for moisture retention and perlite or vermiculite to improve drainage. You can make your own mix with equal parts peat and compost or purchase ready-made organic potting soils (2). For raised beds, you can amend native soil with compost or nutrient-rich topsoil to improve texture and fertility.
Avoid heavy clay garden soils in containers, as these will easily become compacted. Test garden beds for nutrient levels and pH to determine amendments needed to optimize growing conditions. With quality soils tailored to the unique needs of containers and raised beds, urban gardeners can maximize plant health and yields.
Sources:
(1) https://frugalfamilyhome.com/home/gardening/best-soil-for-container-gardening
(2) https://miraclegro.com/en-us/projects-planning/best-soil-to-use-in-containers-and-raised-beds.html
Sunlight and Shade
When designing an urban garden, it’s important to consider how to maximize sunlight while also finding solutions for shaded areas. Most vegetables require at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day, especially fruiting crops like tomatoes, peppers, beans, and squash (The Old Farmer’s Almanac).
For areas that receive less than 6 hours of sun, focus on growing leafy greens and cole crops which can tolerate partial shade. Greens like spinach, lettuce, kale, chard, arugula, and parsley will produce well with 4-6 hours of sunlight (Grow a Good Life). Cole crops like broccoli, cabbage, and bok choy also grow well in partial shade.
When planting in shady areas, choose varieties specifically bred to thrive in low light. Use light reflecting surfaces like white-painted walls to maximize sunlight. Position taller plants to not shade shorter ones. And supplement with grow lights if needed.
With smart planning and plant selections, it’s possible to have a productive urban garden even with sunlight challenges.
Water Systems
An efficient watering system is crucial for urban gardens with limited space. Drip irrigation applies water directly to the soil through tubes or hoses with small openings. This reduces water lost to overspray, evaporation, and runoff. Drip irrigation also lowers the risk of foliar diseases by keeping foliage dry. Compared to sprinklers, drip irrigation uses 20-50% less water while maximizing growth and yield.
Rainwater harvesting is another great option for urban gardens. You can collect rainwater from rooftops or other surfaces into barrels, cisterns, or tanks. This free source of water reduces your dependence on municipal supplies. Just be sure to use rainwater soon after collection, as stored water can promote mosquito breeding. Always follow local regulations for rainwater collection and use.
When designing your garden’s water system, choose high-efficiency components like drip tubing, micro-spray jets, or low-flow pumps. Look for user-friendly timers and controllers to automate watering. Proper installation, spacing, and pressure regulation are also key for optimal performance.
Sources:
Pest Control
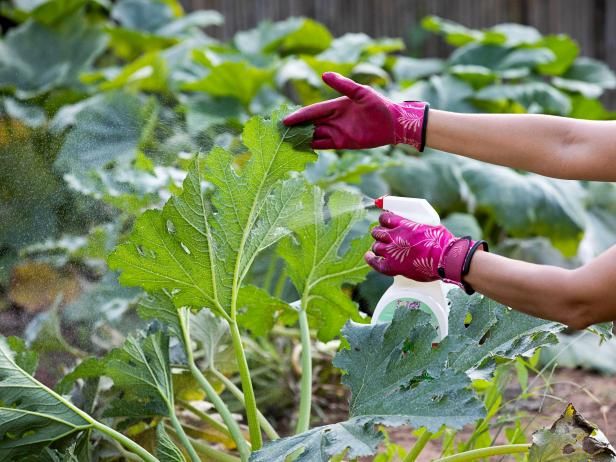
Dealing with pests is one of the biggest challenges for urban gardeners. In tight spaces, pests like aphids, spider mites, cabbage worms, and slugs can quickly get out of control and damage your plants. The good news is there are many organic solutions that don’t require the use of harsh chemicals.

Some of the most common urban garden pests and organic ways to control them include:
- Aphids – Spray plants with a strong stream of water to knock them off, or use insecticidal soap or neem oil (Organic Pest Control for Your Garden That Really Works).
- Spider Mites – Apply neem oil, insecticidal soap or a light horticultural oil (Organic Ways to Treat Pests in a Vegetable Garden).
- Cabbage Worms – Use Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), spinosad or neem oil sprays.
- Slugs – Set out beer traps, lay down abrasive diatomaceous earth or treat with iron phosphate baits.
Other helpful organic prevention and control methods are to remove pest breeding grounds, use row covers, attract beneficial insects, and rotate crops. With some observation and quick action, you can keep pests under control while keeping your urban garden organic.
Plant Selection
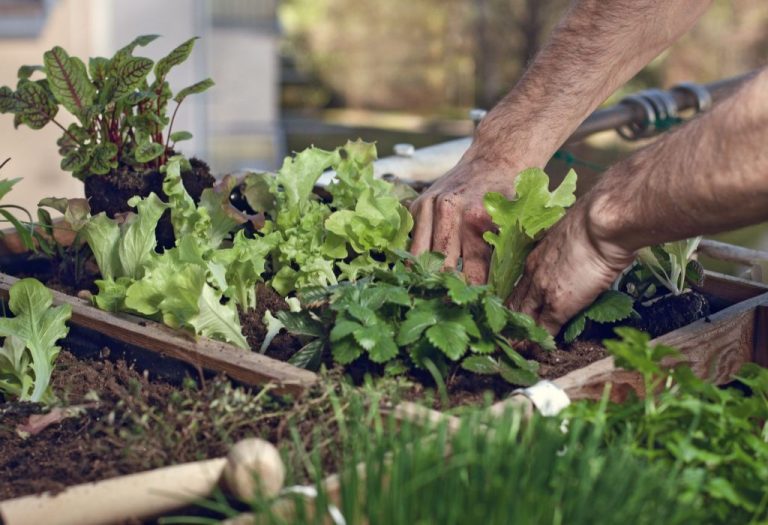
When designing an urban garden, carefully selecting the right plants is crucial for maximizing your limited space. Focus on plants that thrive in containers, are compact or vining, provide edible crops, or can grow vertically.
Good choices for small spaces include herbs like thyme, oregano, chives, and parsley which can be grown in pots on a sunny balcony or windowsill. Leafy greens like lettuce, kale, spinach, and swiss chard are also productive in containers and don’t require much room. For vertical gardening, pole beans, cucumbers, cherry tomatoes, and climbing vines like grapes or kiwi can be trained to grow upwards with the use of trellises (Source).
When choosing edibles, prioritize high-yield dwarf varieties and compact options like bush tomatoes over sprawling indeterminate tomatoes. Radishes, carrots, beets, and strawberries are other good urban edible options. For ornamentals, succulents, flowering annuals, and compact perennials are ideal for small spaces and containers (Source).
By selecting the right small-space specific plants, urban gardens can thrive even with limited square footage.
Season Extension
Extending the growing season allows urban gardeners to grow vegetables for a longer period of time. Popular methods for season extension include greenhouses, cold frames, and fabric row covers.
Greenhouses provide a protected environment that can be heated to keep plants warm during colder months. Small hobby greenhouses can be purchased or built with materials like PVC pipe and plastic sheeting. Greenhouses allow gardeners to grow vegetables like tomatoes and peppers year-round.
Cold frames are essentially small unheated greenhouses, usually made out of wood, that sit directly on top of the garden bed. The glass or plastic lid traps heat from the sun during the day. Plants inside are protected from wind and frost at night (see Season-Extending with Row Covers and Cold Frames). Cold frames work well for cool weather crops like lettuce, spinach, and carrots.
Fabric row covers are lightweight polyethylene fabrics that drape directly over plants, shielding them from cold temperatures. Row covers allow sunlight and water to pass through. Plants under row covers can withstand temperatures around 25 degrees lower than uncovered plants (see 7 Ways to Extend the Growing Season).
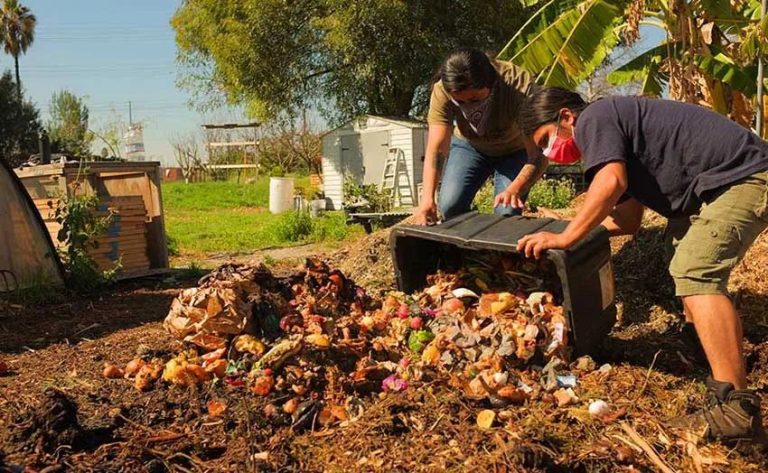
Composting
Composting is an important part of any urban garden as it recycles nutrients and provides free fertilizer for plants. There are several small-scale methods that work well for urban composting including worm composting, compost tumblers, and vermicompost.
Worm composting, also known as vermicomposting, uses red wiggler worms to break down food scraps into an excellent fertilizer called worm castings (Small Scale Composting). Worm bins can be purchased or homemade using plastic storage bins. The worms feed on vegetable and fruit scraps, coffee grounds, and shredded paper. Their castings contain nutrients plants thrive on.
Compost tumblers (Backyard Composting Using Simple, Small-scale Methods) are enclosed bins that can be rotated or tumbled to aerate the compost. By frequently mixing the contents, decomposition happens faster than static compost piles or bins. Compost tumblers take up little space and keep out pests.
Vermicompost uses worm castings as a nutrient-rich soil amendment or mulch. Worm castings contain many nutrients plants need including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and micronutrients. Vermicompost helps condition soil and increases its water holding capacity (Backyard Composting Using Simple, Small-scale Methods).
Conclusion
Urban gardening allows city dwellers to grow their own fresh fruits, vegetables, and herbs even with limited space. The key ideas covered in this article demonstrate that urban gardens can thrive with careful planning and innovation. From utilizing vertical space and containers to controlling sunlight, water, and pests – there are many practical solutions for a productive urban garden.
The benefits of gardening in an urban setting are plentiful. It provides a connection to nature amidst the concrete jungle. You have control over what you grow and can ensure it’s free of chemicals. Urban gardens allow you to harvest the freshest ingredients right outside your door. It’s an enjoyable hobby that relieves stress. And it provides food security and saves money at the grocery store.
With some creativity and dedication, anyone can design a flourishing urban garden. The ideas presented give urban dwellers the tools to grow healthy fruits, veggies, and herbs despite limited yard space. Urban gardening is a rewarding experience that allows city residents to tap into their green thumbs.